Chikungunya and dengue is a growing health concern across the world. A person may contact the chikungunya virus through the bite of an mosquito. Read on to know more.
Chikungunya is a growing health concern across the world. A person may contract the chikungunya virus through the bite of an infected mosquito. The defining characteristic of Chikungunya is the extreme joint pain it causes, and although the infection itself only lasts for between two and twelve days, the joint pain can last for several months. Thankfully, this disease is preventable as certain precautionary measures can be taken to prevent the mosquito bites which cause the illness.
Controlling Mosquito Populations
1. Know that chikungunya fever is contracted through mosquito bites.
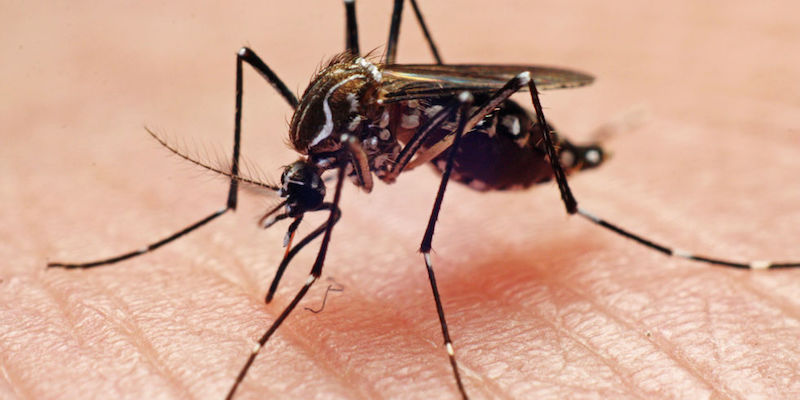

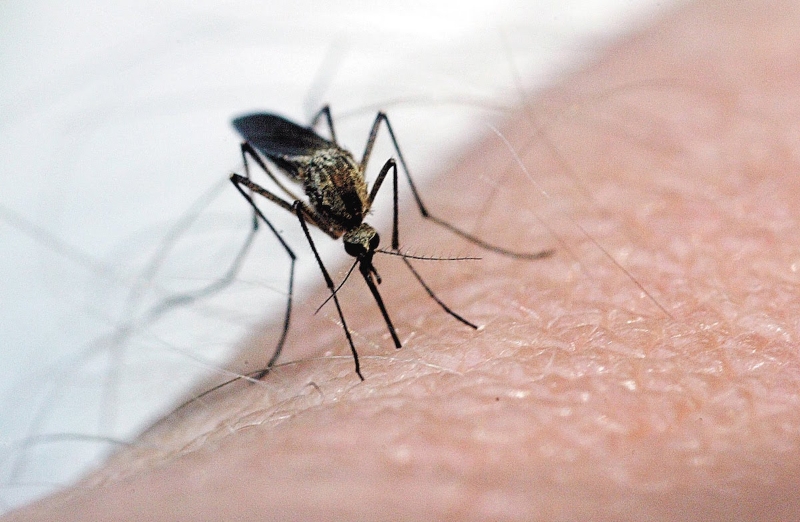
The virus that causes chikungunya fever is from the genus Alphavirus. This virus is transmitted to humans through mosquito bites, most commonly those of the Aedes aegypti mosquito.
Aside from chikungunya, the Aedes aegypti mosquito can transmit other diseases such as dengue and yellow fever.
The Aedes aegypti mosquito can easily be identified by the unique white markings on its legs and body. Originally, this mosquito was only found in Africa, but now it is found in subtropical and tropical regions across the globe.
The mosquito is attracted to human blood by certain chemical compounds emitted by the body, such as ammonia, lactic acid, carbon dioxide, and octenol.
2. Familiarize yourself with the behavior of the mosquito.
The Aedes aegypti mosquito is known to be more active during the early and late hours of the day.
However, these mosquitoes can bite at any time of the day and in any season. In addition to this, Aedes aegypti is more common in dark, shady areas, and indoors.[3]
The most common breeding area of Aedes aegypti is stagnant water. This includes the water found in flower vases, discarded tires, buckets, uncovered barrels, bottles, and others.
The lifespan of Aedes aegypti may last up to one month. However, its eggs are resistant to cold and heat. Thus, these mosquitoes can easily make a comeback after the summer and winter.
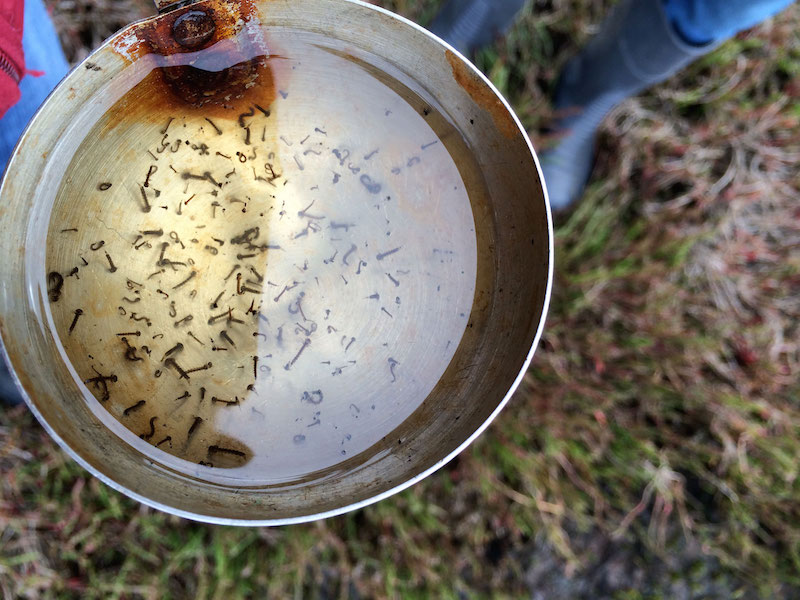

One of the best ways to protect yourself from chikungunya virus is to go directly to the mosquito's breeding grounds and eliminate as many mosquitoes and eggs as possible.
The most common breeding area for the Aedes aegypti mosquito is standing water. Therefore, the first step is to empty any open containers of water around your home.
Next, look for any possible reservoirs of water around your home or backyard that may serve as a place for mosquitoes to reproduce. This may include discarded tires, flower vases, cans, bottles, rain gutters, drums, and more.
4. Perform general cleaning around your home or community.
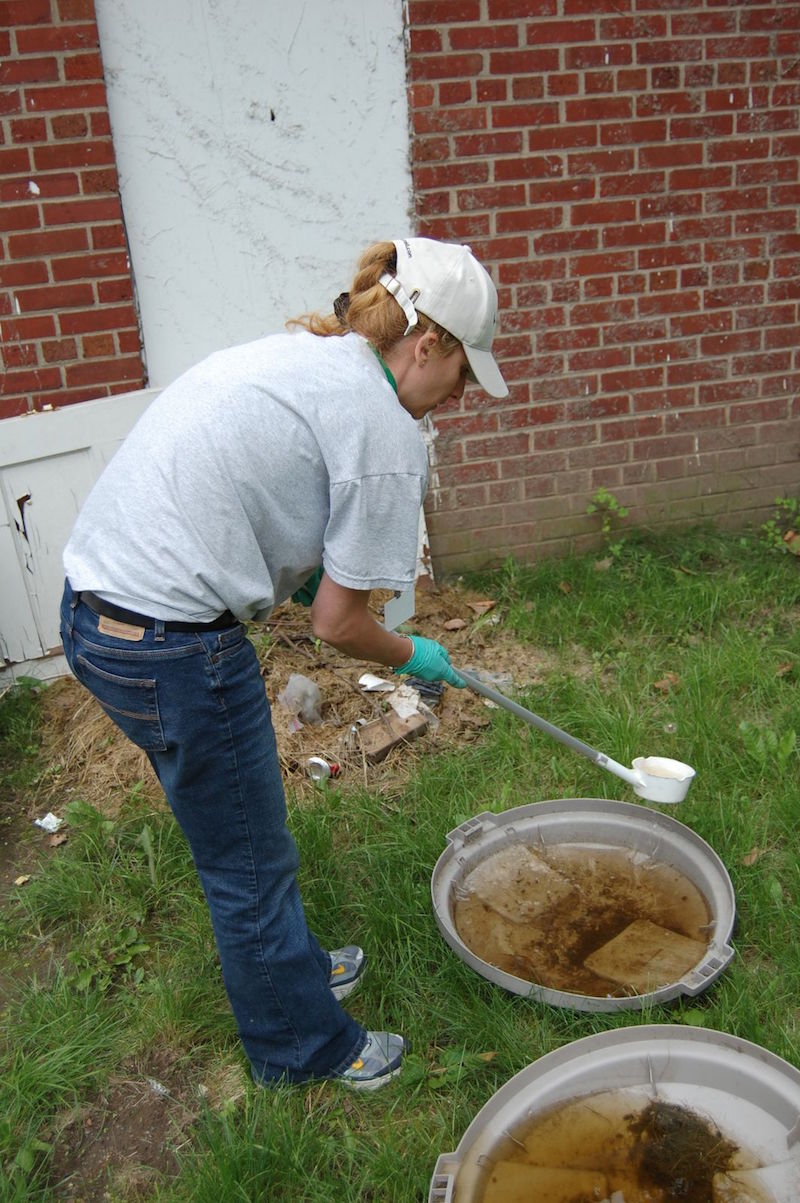

It should be noted that female Aedes aegypti are attracted to the scent of bacteria found in stagnant water, so when you clean your surroundings, there will be less stagnant water and therefore fewer mosquitoes.
Cleanliness is the key to destroying the homes of mosquitoes, therefore you should make sure that you clean your water drainage system. Also keep in mind that stagnant rivers, creeks, or canals may also serve as a breeding ground for these mosquitoes.
In the event that a creek or river is filled with plants or garbage to the point that the water cannot flow anymore, make a concerted effort with your community to implement a clearing program which will get the water flowing again.
5. Add some fish to ponds or any other bodies of water.

Fish are great for keeping mosquitoes under control. Since ponds and other still bodies of water may attract Aedes aegypti, adding fish to the water will help to decrease the number of mosquito eggs and larvae as they will be eaten by the fish. This method may serve as a long-term solution for mosquito control.
The most common type of fish that feeds on mosquitoes is the Gambusia affinis, better known as the mosquitofish. Other fish may include minnow, carp, tilapia, and killfish.
You should also promote populations of other animals that prey on mosquitoes. This includes lizards, geckos, dragonflies, frogs, birds, bats, and others.
6. Use mosquito traps.
Mosquito traps involve the creation of an artificial breeding ground for the Aedes aegypti mosquito. Then, once the mosquitoes have laid their eggs, the eggs can be destroyed manually or special chemicals can be added to the traps to kill the larvae.
The most common mosquito trap is the lethal ovitrap. Originally, this type of trap was used to study mosquito populations, but it was later found that scientists could simply add chemicals to the trap to kill both the eggs and the larva. Lethal ovitraps are effectively used to protect against chikungunya, yellow fever, dengue fever, and west Nile virus.
A light trap is another good mosquito control device. A blue or violet colored UV light is used to attract the mosquitoes. Once inside the trap, the insects are either electrocuted or are caught in a sticky board.
Recognizing Symptoms of Chikungunya
1. Look for swelling, redness and pain in the joints.
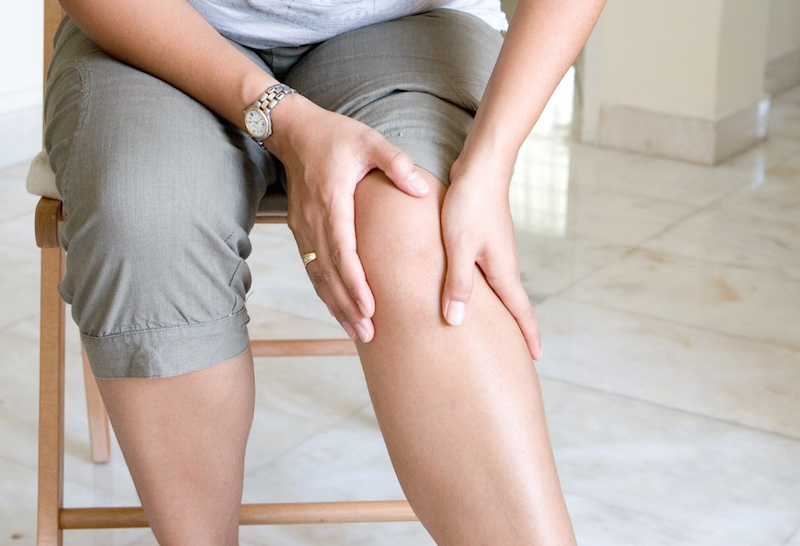

People infected with chikungunya will experience severe pain in the joints, especially in the joints of the lower limbs such as the ankles, knees and hip joints and in the joints of the upper limbs such as elbows, shoulders and wrists. Backache is rarely seen with this disease.
The joint pain is often described as aching or throbbing in nature. Redness and swelling are also present in addition to the joint pain. The joint will be very tender to the touch and the sufferer may have difficulty in moving their joints.
Sometimes, the sufferer may be unable to move their joints due to severe pain, causing difficulties in walking, standing up from a sitting position , running, writing, driving, picking things up, etc.
2. Watch out for secondary symptoms.
Aside from joint pain, secondary symptoms of chikungunya fever include nausea, vomiting, conjunctivitis, and photophobia (hypersensitivity to light). Sometimes, a person's sense of taste is also affected.
3. Understand the progression of the symptoms.
In its initial stages, chikungunya fever presents itself with symptoms such as:
Low grade fever or increased body temperature, malaise, a reduction in feelings of hunger etc. Sometimes vomiting is also present.
After five to seven days, the joint pain begins. It starts with mild difficulties in movement and pain in the joints early in the morning. The patient may even have difficulty getting out of bed. However, this pain should start to subside as the day progresses.
There is an ongoing effort to create a chikungunya vaccine. To some extent, the existing vaccine is effective, but only for a limited length of time. Studies show that the vaccine is only effective for less than a year. In addition to this, some people reported that they experienced signs and symptoms associated to chikungunya even after being vaccinated.
Prevention is always better than cure; and this is certainly true when it comes to chikungunya. Make sure you follow the steps above to increase your chance of evading this unpleasant disease.
Source : wikiHow