Best Electrical Solutions for Healthcare Facilities
Electricity in healthcare isn’t just about lights—it ensures safety, reliability, and seamless patient care where every second matters.
Healthcare facilities demand more than just clean hallways and modern equipment. Behind the walls and ceilings, an electrical system quietly decides how smoothly everything runs. A hospital that suffers an electrical failure is not just inconvenienced, it risks lives. That’s why the way we design, maintain, and upgrade these systems matters as much as the skill of the doctors and nurses walking the halls.
I’ve walked through more than a few healthcare environments where the hum of machines felt louder than the conversations. And in those moments, I’m always reminded that electricity in healthcare isn’t just about lights staying on. It’s about patient safety, reliability, and creating a steady environment for patients and staff.
Why Electrical Infrastructure Matters in Healthcare Facilities
Most people never think about the electricity that keeps a hospital alive. They notice the waiting rooms or maybe the cafeteria coffee, but not the systems keeping life-support equipment powered. Healthcare facilities use more energy per square foot than most commercial buildings. The U.S. Energy Information Administration has reported that inpatient hospitals account for nearly 68% of healthcare electricity use nationwide. That’s staggering.
The reason is obvious when you think about it. Critical medical equipment, imaging technology, labs, and HVAC systems operate nonstop. This makes a reliable electrical system essential for patient care. A single power outage can interrupt surgeries, delay treatments, and even put lives at risk. Facility managers carry this weight on their shoulders every day.
Healthcare facilities depend on a stable electrical system not just for lighting or comfort, but to sustain life-critical equipment and essential operations. When the system fails, the risks are immediate and severe. As FEMA highlights, “Loss of electrical power can severely disrupt healthcare facility operations, potentially jeopardizing patient safety and the delivery of essential medical services.” That reality underscores why facility managers must prioritize not just day-to-day reliability but also resilience during crises.
Core Elements of a Reliable Electrical System
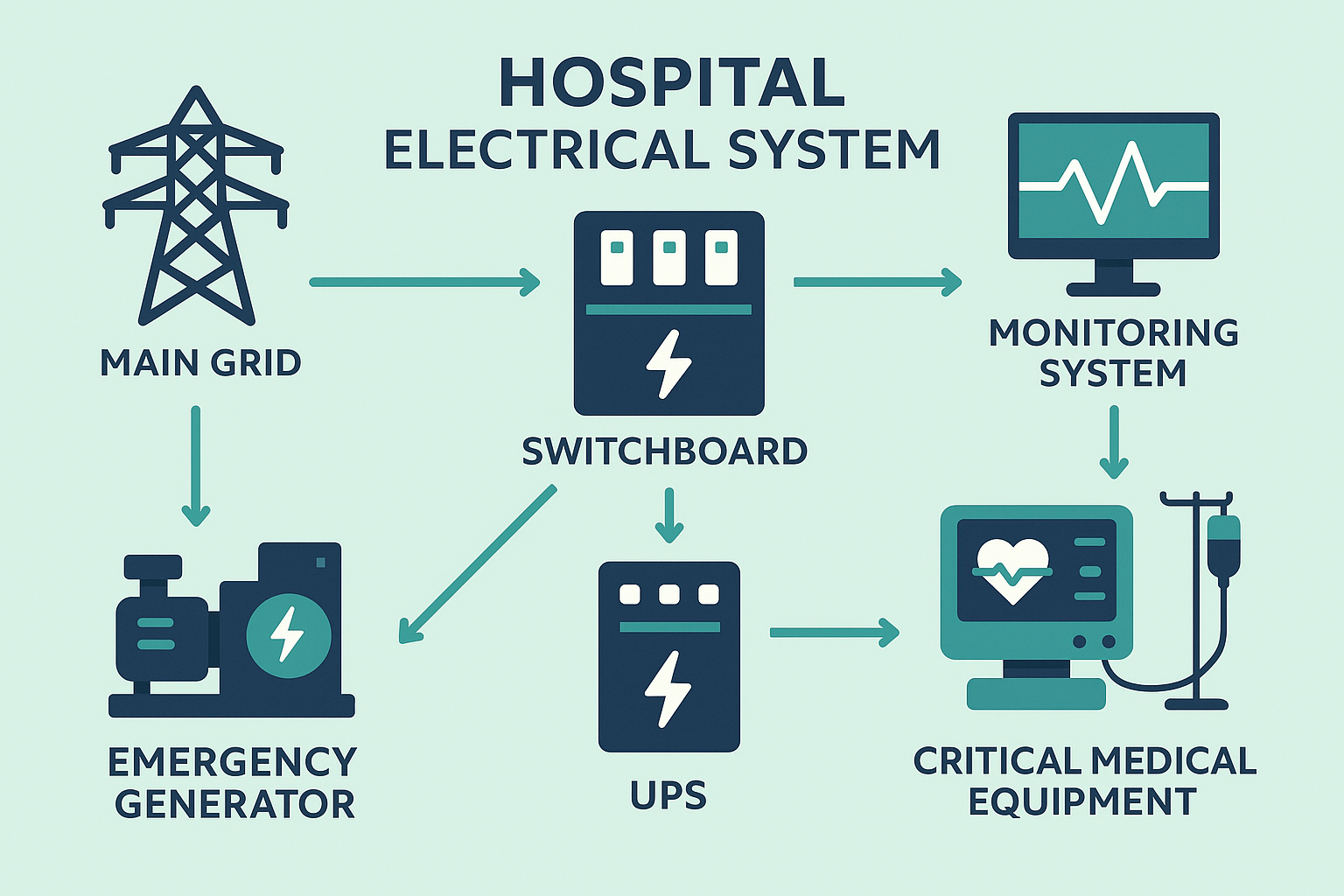
An electrical system in a healthcare setting has more layers than an ordinary office building. You don’t just run wiring and outlets. You build redundancy and protection into every step.
Power Distribution and Switchboards
Modern healthcare facilities need switchboards that can handle heavy loads and redirect electricity quickly if a fault occurs. Without them, operational efficiency suffers and critical zones could lose power. I once visited a clinic where the staff had to juggle which imaging machine ran at which time, simply because their distribution panel couldn’t handle simultaneous demand. It sounds unbelievable today, but it still happens.
Emergency Power Systems and Automatic Transfer Switches
When a storm hits or the grid stumbles, an automatic transfer switch ensures backup generators kick in instantly. These devices may seem small, but they separate hospitals from disaster during a blackout. The faster the switch, the more uninterrupted power supply is guaranteed. Some newer designs have reduced their footprint by half while also making maintenance safer for technicians. That means less downtime and less risk.
Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) Units
A generator may take seconds to activate, but seconds are enough to crash monitoring systems or delicate machines. UPS units fill that gap. They provide uninterrupted power that bridges the handoff, protecting patients during those crucial moments. A cardiologist once told me she still remembers the sound of an old UPS clicking on during a surgery. That click gave her confidence, because she knew someone had planned for the worst.
Circuit Protection and Monitoring Systems
Smart monitoring systems track usage patterns, anticipate surges, and alert staff before electrical failures occur. Combined with protective devices, they ensure the safety of both staff and patients. It’s not glamorous work, but when you think about what’s at stake, nothing could be more essential for patient outcomes.
Data, Demand, and Load Management
One of the biggest challenges in designing electrical services for hospitals is that the codes often oversize demand. A large national study found that actual healthcare facility loads are less than half of what the current code requirements suggest. In other words, engineers are often planning for a peak that never comes. That sounds safe, but it wastes space, materials, and money.
With the help of AI and real-time data, we can now predict demand with far greater accuracy. Machine learning models, for example, have achieved error rates under 10% in forecasting hospital power system loads. That means facility managers can design for the real needs of healthcare, not inflated estimates. This makes upgrades more affordable and tailored to actual usage.
Plug loads are another area worth watching. In a typical hospital, plug loads average about 1 watt per square foot, rising to 2 in intensive care or imaging suites. These numbers might sound small, but when multiplied across an entire campus, they shape the design of a reliable power system.
Building Energy Efficiency into Healthcare Facilities

Healthcare environments consume a tremendous amount of energy for heating, cooling, and lighting. HVAC alone can account for more than half of the electricity use in some facilities. That’s why efficiency measures aren’t just about saving money, they’re about making the environment for patients more comfortable and reliable.
Some of the most effective strategies include high-efficiency HVAC systems, LED lighting with smart controls, and energy benchmarking to track performance over time. A few years ago, I walked into a recently renovated facility where every corridor used LEDs paired with occupancy sensors. Staff told me the space felt brighter, yet their energy bills had dropped noticeably. That’s the kind of win hospitals need.
There’s also a connection between efficiency and patient health. Better lighting, thermal comfort, and indoor air quality all play into recovery and staff performance. Your hospital’s uptime relies on expert commercial electrical service to maintain patient-critical systems. Energy efficiency, then, isn’t just a numbers game, it is essential for patient care.
Case Studies That Show the Difference
Theories are useful, but I prefer examples. One major medical center shaved five months off its construction timeline by adopting more compact switchgear. The decision also reduced footprint and simplified maintenance, making it safer for electricians. That’s operational efficiency in action.
Another case involved upgrading outdated single-line diagrams with modern software mapping. The result was faster installations, easier maintenance, and improved collaboration among teams. The staff mentioned they no longer wasted hours cross-referencing old schematics. It was an upgrade that paid for itself.
UPS installations also stand out. A facility that added UPS support to its imaging suites reported zero interruptions across a full year, despite multiple local grid disturbances. That level of reliability may never make the news, but it absolutely protects patients.
The Human Side of Reliable Power
I’ve had conversations with facility managers who describe their job as invisible until something goes wrong. That might be true, but in healthcare settings their work is absolutely essential for patient well-being. Every choice about power supplies, monitoring systems, or maintenance schedules ultimately ties back to how we protect patients.
There’s also the matter of compliance. Safety standards are not optional. NFPA 70B, for instance, outlines preventive maintenance requirements that directly impact electrical safety. Falling behind on inspections or skipping tests may not show consequences today, but it invites risk tomorrow. A reliable electrical system is as much about discipline as it is about technology.
Recommendations for Facility Managers

- Conduct regular electrical audits and energy assessments.
- Plan upgrades with accurate load data, not outdated assumptions.
- Invest in UPS systems to guarantee uninterrupted power supply during transitions.
- Use switchboards and transfer switches designed for healthcare facilities, not generic commercial buildings.
- Monitor plug loads and track patterns through smart monitoring systems.
- Prioritize energy efficiency in HVAC and lighting without compromising safety.
- Train staff and schedule preventive maintenance that meets safety standards.
These aren’t abstract recommendations. They’re the practical steps I’ve seen make the difference between a hospital that struggles with outages and one that delivers seamless patient care.
Conclusion
The electrical system inside healthcare facilities is more than wires and breakers. It is the silent backbone that keeps critical medical equipment running, ensures the safety of patients, and allows caregivers to focus on their work without fear of power outages.
When we talk about reliable electrical design, we are really talking about creating an environment for patients that is safe, stable, and capable of handling anything. From power supplies to monitoring systems, every decision shapes patient care and the ability to protect patients during the most vulnerable moments.
Electrical services in healthcare are never just technical. They are human, rooted in trust, and essential for patient outcomes. And for facility managers, investing in a reliable power system is not just good practice, it is the responsibility that keeps modern healthcare alive.



Comments ()