An Essential Guide to LED Lighting in Residential Applications
LED lights are rising in popularity for their energy-saving, long-lasting, and versatile features. It's crucial to know the pros, cons, and how to pick the right LEDs.

LED lighting has gained popularity in recent years due to its energy efficiency, longevity, and versatility in both residential and commercial applications. As the demand for LED lighting continues to grow, it's important for homeowners to understand the benefits and drawbacks of this lighting technology, as well as how to choose the right LED lighting for their homes.
This essential guide to LED lighting in residential applications provides homeowners with the information they need to make informed decisions about their lighting choices. The guide covers a range of topics, including the basics of LED lighting, such as brightness, light appearance, and color rendering, as well as the advantages of LED lighting over traditional incandescent bulbs. Additionally, the guide explores the various types of LED bulbs available, such as dimmable bulbs, floodlights, and smart bulbs, and how they can be used throughout the home.
Whether you're looking to reduce your energy bills, enhance the ambiance of your home, or simply upgrade your lighting, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools you need to make the most of LED lighting in your residential space.
The Basics of LED Lighting
LED lighting is becoming increasingly popular in residential applications due to its energy efficiency, longevity, and versatility. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs, LEDs use a semiconductor to convert electricity into light, making them more energy-efficient and long-lasting. In this section, we will cover the basics of LED lighting and what you need to know before making the switch.

Light Source
LEDs are a type of solid-state lighting that emits light when a current is passed through a semiconductor. Unlike incandescent bulbs, which produce light by heating a filament, LEDs emit light through a process called electroluminescence. This process allows LEDs to be more energy-efficient and long-lasting than traditional bulbs.
Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of LED lighting is its energy efficiency. LEDs use significantly less energy than traditional bulbs, making them more cost-effective in the long run. Additionally, LEDs emit less heat than traditional bulbs, making them safer and more comfortable to use.
Quality of Light

LEDs are available in a range of colors and color temperatures, from warm white to cool daylight. The color temperature of an LED is measured in Kelvin (K), with lower numbers indicating warmer light and higher numbers indicating cooler light. It is essential to choose the right color temperature for your needs, as it can affect the atmosphere of a room.
Brightness
LED lighting is measured in lumens, not watts. This means that the brightness of an LED bulb is not directly related to its wattage, as it is with traditional bulbs. Instead, the brightness of an LED bulb is determined by its lumens rating. When choosing an LED bulb, it is essential to consider the lumens rating to ensure that it provides the right amount of light for your needs.
Lifetime

One of the most significant benefits of LED lighting is its long lifetime. LED bulbs can last up to 25 times longer than traditional bulbs, making them a cost-effective choice in the long run. Additionally, LED bulbs are more durable than traditional bulbs, making them less likely to break or fail.
Intensity
LEDs are directional light sources, which means they emit light in a specific direction. This makes them ideal for task lighting and accent lighting, as they can provide bright, focused light where it is needed. Additionally, LEDs can be dimmed to provide the right level of light for any situation.
Comparing LED Lighting with Traditional Lighting Technologies
LED lighting has become increasingly popular in recent years, especially in residential applications. One of the main reasons for this is its energy efficiency. Compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, LED lights consume significantly less energy, which translates to lower electricity bills and reduced environmental impact.
The energy efficiency of LED lighting is measured in lumens per watt (LPW). LPW is a measure of how much light is produced per unit of energy consumed. LED lights typically have a higher LPW than traditional lighting technologies, such as incandescent bulbs, CFLs, and fluorescent lights. This means that LED lights produce more light per unit of energy consumed, making them more energy-efficient.
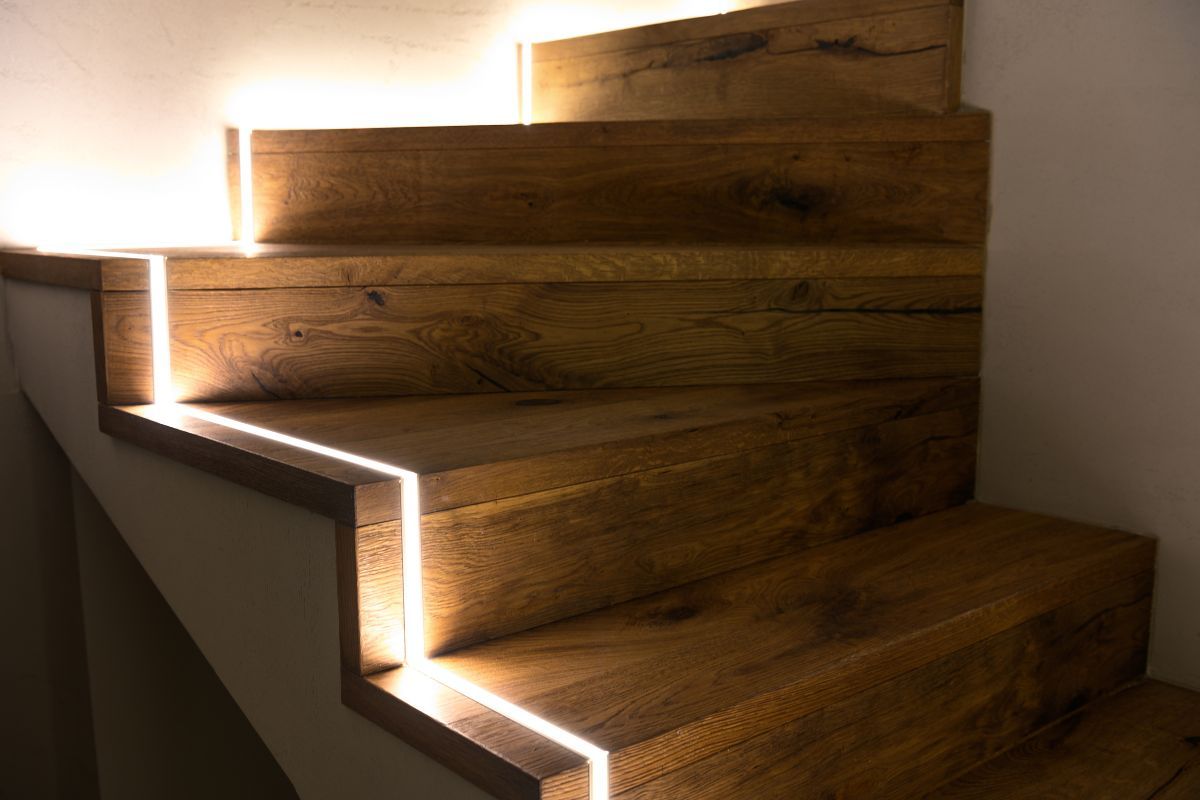

LED lighting is also comparable in terms of light output to traditional lighting technologies. For example, a 60-watt incandescent bulb produces around 800 lumens of light, while a 10-watt LED bulb produces the same amount of light. This means that LED lights can replace traditional lighting technologies without sacrificing light output.
In addition to energy savings, LED lighting has other advantages over traditional lighting technologies. For example, LED lights have a longer lifespan than traditional incandescent bulbs. LED lights can last up to 25,000 hours, while traditional incandescent bulbs typically last only around 1,000 hours. This means that LED lights need to be replaced less frequently, reducing maintenance costs.
LED lights also produce less heat than traditional incandescent bulbs. This means that they are safer to use and can help reduce cooling costs in hot climates. LED lights are also more durable than traditional incandescent bulbs and are less likely to break.
LED Lighting Design and Applications in Residential Settings
LED lighting has become increasingly popular in residential settings due to its energy efficiency, long lifespan, and versatility. LED lighting can be used for a variety of applications in residential settings, from task lighting to decorative lighting.
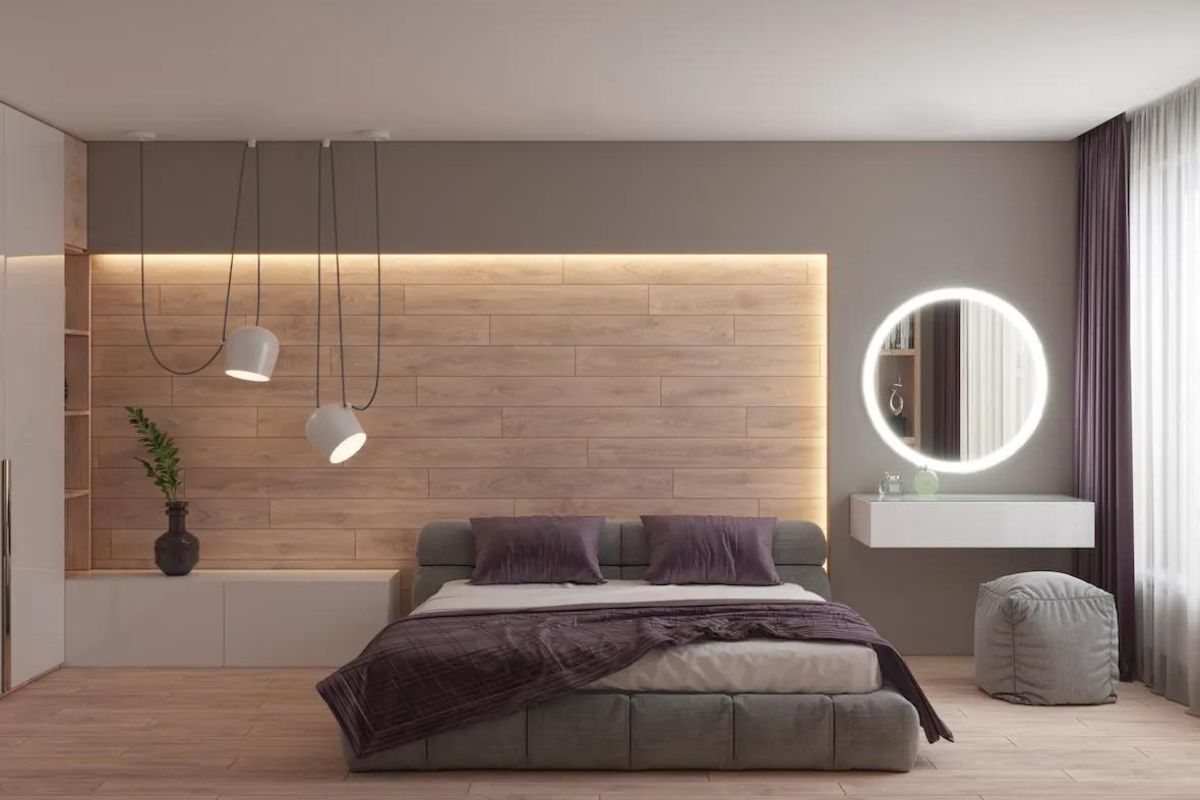

Designing an LED lighting system for a residential setting requires careful consideration of the space, the desired lighting effect, and the homeowner's needs. Builders and homeowners should consider the following factors when designing an LED lighting system:
- Task Lighting: Task lighting is an important aspect of residential lighting design. LED under-cabinet lighting is a popular choice for kitchens, providing bright, focused light for food preparation and cooking. LED recessed downlights are also commonly used for task lighting in living areas, bedrooms, and bathrooms.
- Ambient Lighting: Ambient lighting is used to create a warm, inviting atmosphere in a room. LED strip lighting is a popular choice for ambient lighting, providing soft, indirect light that can be used to highlight architectural features or provide a subtle glow in a room.
- Decorative Lighting: Decorative lighting is used to add visual interest to a space. LED pendant lights and chandeliers are popular choices for decorative lighting in living areas and dining rooms.
- Energy Efficiency: LED lighting is more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent lighting, making it a popular choice for homeowners looking to reduce their energy consumption and save money on their electricity bills.
- Long Lifespan: LED lighting has a longer lifespan than traditional incandescent lighting, reducing the need for frequent bulb replacements.
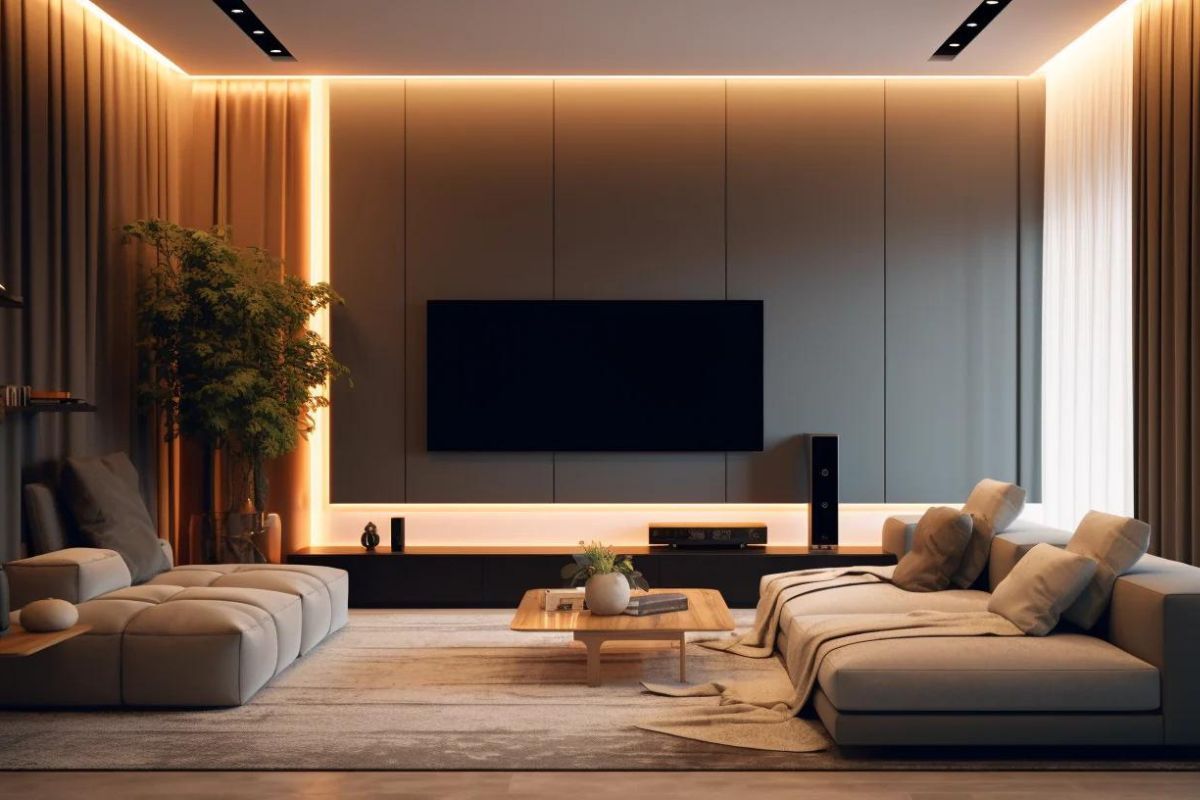

In addition to these factors, builders and homeowners should also consider the specific needs of each room when designing an LED lighting system. For example, bathrooms require bright, focused lighting for grooming and makeup application, while bedrooms require softer, more relaxing lighting.
Understanding and Choosing the Right LED Products
LED lighting is becoming increasingly popular in residential applications due to its energy efficiency, versatility, and long lifespan. However, with a wide range of LED products available, it can be challenging to choose the right manufacturer or product for your needs. In this section, we will provide an overview of the most important factors to consider when selecting LED lighting products for residential applications.
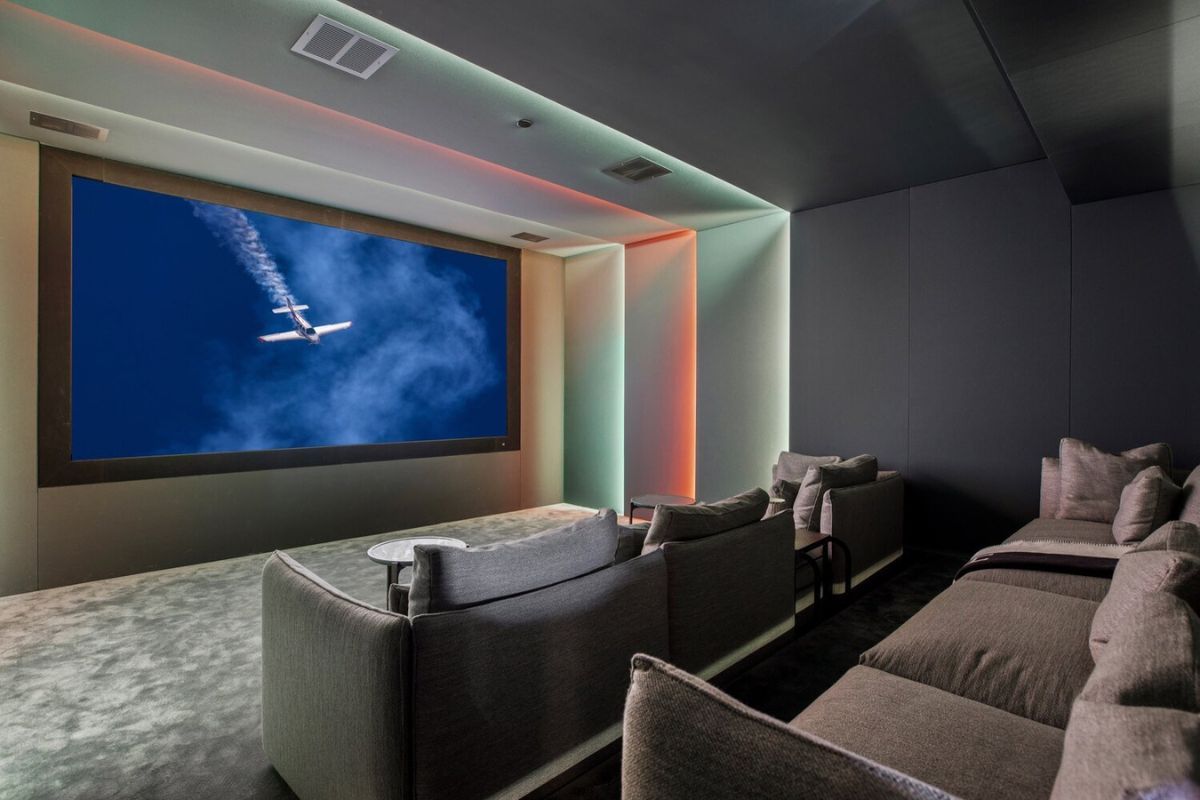

LED Light Sources
LED light sources are available in a variety of shapes and sizes, including bulbs, tubes, and strips. LED bulbs are a popular choice for residential lighting because they can be used to replace traditional incandescent bulbs, while LED tubes are commonly used in commercial lighting applications. LED strip lights are versatile and can be used to create a variety of lighting effects, such as under-cabinet lighting or accent lighting.
Color Temperature and Color Rendering Index
When selecting LED lighting products, it is essential to consider the color temperature and color rendering index (CRI). Color temperature refers to the color of the light emitted by the LED, with lower temperatures producing warm, yellowish light and higher temperatures producing cool, bluish light. The CRI measures how accurately the LED light source renders colors compared to natural light. A higher CRI means that colors will appear more vibrant and true to life.
High-Efficacy Luminaires
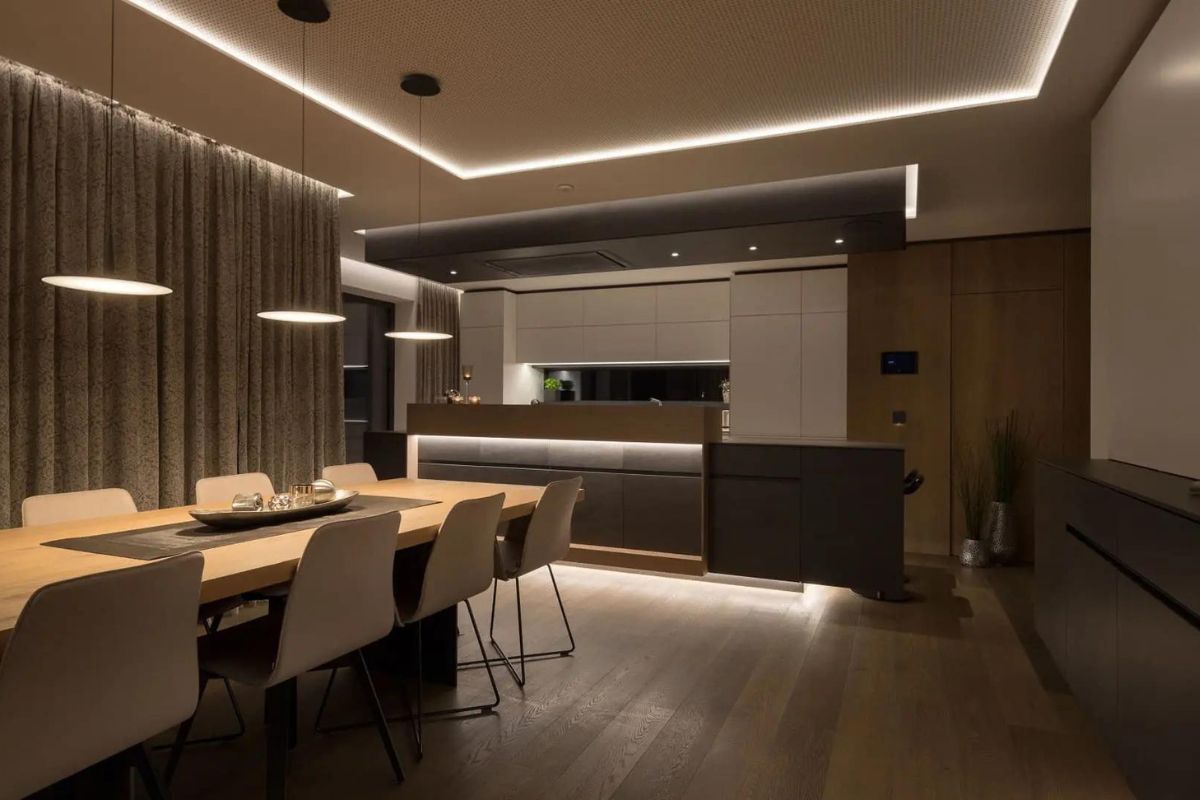

High-efficacy luminaires are lighting products that meet specific energy efficiency requirements. These products are designed to provide high-quality lighting while using less energy than traditional lighting products. When selecting LED lighting products, it is important to choose high-efficacy luminaires to maximize energy savings and reduce environmental impact.
Lighting Controls
Lighting controls can be used to adjust the brightness and color temperature of LED lighting products, making them more versatile and customizable. Dimmer switches, timers, and motion sensors are all examples of lighting controls that can be used to improve energy efficiency and enhance the functionality of LED lighting products.
Lithonia Lighting

Lithonia Lighting is a leading manufacturer of LED lighting products for residential and commercial applications. Their products include a wide range of high-quality LED luminaires, including indoor and outdoor fixtures, strip lights, and more. Lithonia Lighting products are designed to provide reliable, long-lasting performance while reducing energy consumption and minimizing environmental impact.
Installation and Fitting of LED Lighting
Installing LED lighting in residential applications is a simple process that can be done by anyone with basic electrical knowledge. However, for those who are not comfortable working with electricity, it is recommended to hire a licensed electrician to ensure proper installation.

LED lights are designed to fit into existing light fixtures, making installation and fitting a breeze. They are available in a variety of shapes and sizes, including bulbs, strips, and panels, and can be used in almost any application.
One of the benefits of LED lighting is that they are compatible with dimmer switches, allowing users to adjust the brightness of the light to their preference. However, it is important to note that not all LED lights are compatible with all dimmer switches, so it is important to check the compatibility before installation.
LED lights are also more durable and longer lasting than traditional incandescent bulbs, making them a popular choice for residential applications. They are resistant to shock and vibration and have a longer lifespan, which means less maintenance and replacement costs in the long run.
Regulations and Standards for LED Lighting
LED lighting has become increasingly popular in residential applications due to its energy efficiency, long lifespan, and versatility. However, there are regulations and standards in place to ensure that LED lighting is safe and effective for consumers.

One of the most well-known regulations for LED lighting is Title 24, which is California's energy code. Title 24 sets energy efficiency standards for buildings and appliances, including lighting. In particular, Title 24 has specific requirements for LED lighting in low-rise residential buildings and high-rise residential building dwelling units, which can be found in Chapter 6 of the California Energy Code.
The Department of Energy (DOE) also plays a role in regulating LED lighting. The DOE's Lighting Facts program provides a voluntary labeling system for LED lighting products, which includes information such as lumens, watts, and color temperature. The program aims to help consumers make informed decisions and encourage the adoption of energy-efficient lighting. Additionally, the DOE's Solid-State Lighting program conducts research and development to advance LED lighting technology and improve its performance.

Energy Star is another program that regulates LED lighting. Energy Star is a voluntary program that sets energy efficiency guidelines for various products, including LED lighting. LED lighting products that are Energy Star certified meet strict energy efficiency criteria and are tested for quality and performance.
In addition to these specific regulations and programs, there are also various standards that LED lighting must meet. For example, the Illuminating Engineering Society (IES) has developed standards for LED lighting, including the LM-79 standard for measuring LED lighting performance and the TM-21 standard for predicting LED lighting lifespan. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) has also developed standards for LED lighting, including safety standards and performance standards.
The Impact of LED Lighting on Energy Consumption
LED lighting is one of the most energy-efficient lighting options available in the market today. According to the Department of Energy, LEDs use at least 75% less energy than incandescent bulbs and can last up to 25 times longer. This means that using LED lighting can significantly reduce energy consumption in residential applications.
In addition to being more energy-efficient, LED lighting also has a lower impact on the environment. LED bulbs contain no hazardous materials, unlike fluorescent bulbs, which contain mercury. This makes LED lighting a safer and more sustainable option for residential applications.
Moreover, LED lighting can also help reduce energy costs. Although LED bulbs may be more expensive upfront, they have a longer lifespan, which means that homeowners do not need to replace them as often. Additionally, LED bulbs produce less heat, which can reduce cooling costs during the summer months.
The Future of LED Lighting Technology
LED lighting technology has come a long way since its inception. The future of LED lighting technology looks promising with advancements in various aspects of lighting technology.
One of the most exciting advancements in LED lighting technology is the development of Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs). OLEDs are a type of LED that emits light through an organic material. These materials are thin, flexible, and can be made into any shape or size. OLEDs offer a higher color accuracy and a wider spectrum of colors than traditional LEDs. They also have the potential to be more energy-efficient than traditional LEDs.
Another area of development in LED lighting technology is the integration of smart technology. Smart LED lighting systems can be controlled through a smartphone app or voice-activated assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant. They can be programmed to turn on and off at specific times or in response to certain events. Smart LED lighting technology also has the potential to be integrated with other smart home devices, such as security systems and thermostats.
The future of LED lighting technology also includes advancements in color accuracy. LED lighting manufacturers are working to improve color rendering, which is the ability of a light source to accurately render colors. This is especially important in residential applications, where accurate color rendering can affect the mood and ambiance of a room.



Comments ()